Sometimes it may be needed to organize a DMZ host in your Keenetic local network. It can be a web server, a network video recorder, an IP camera or another device with all ports opened and thus with full remote access to it from the Internet. A DMZ host is not a DMZ segment because a host with open ports is not isolated from the internal network and is not protected by built-in security features (firewall and NAT).
NOTE: Important!
1. Port forwarding will only work if the router uses a public IP address to access the Internet. You will find more information in the article 'What is the difference between a public and private IP address?'
2. The example shown in this article is a special case and not the best option from the connection security point of view. Use this option only if you do not know which ports and protocols are used on a server or network device. In this case, security should be performed directly by means of a device where all ports are open. We recommend that you only open certain ports and protocols in port forwarding necessary for the server or network device to function.
Before setting up the port forwarding rule, register the device in your Keenetic on the 'Device lists' page and enable the 'Static IP' option by specifying the local IP address for this host.
Then, on the 'Port forwarding' page, create a forwarding rule for all ports.
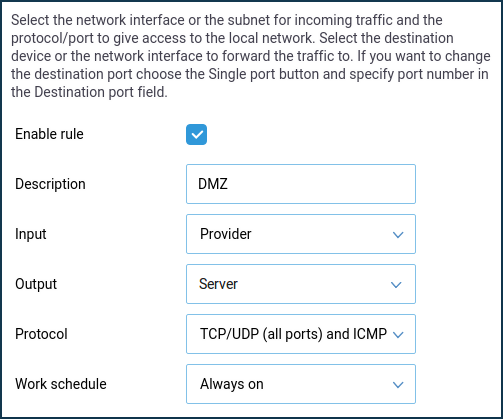
Enable the port forwarding rule.
In the 'Input' field, you should correctly specify the value. Select the connection or interface through which the Keenetic router accesses the Internet and uses a public IP address (in our example, 'Provider'). In most cases, you should select the 'Provider' interface. If you are connected to the Internet via a PPPoE, PPTP or L2TP, you should select the appropriate connection.
In the 'Output' field, select the device, connection or interface to which the appropriate traffic will be forwarded (in our example, it is a computer named 'Server' registered in the home network).
In the 'Protocol' field, select the value 'TCP/UDP (all ports and ICMP)' from the predefined list (this value is the first in the list).
In the 'Work schedule' field, you can add a schedule, according to which this rule will work.
NOTE: Important! When using the forwarding rule, you don't need to configure the firewall as the router opens access to the specified ports and protocols by itself.
If port forwarding does not work, please refer to the article 'What to do if port forwarding does not work'.