Access to the Keenetic management, to its web interface, from the Internet is blocked by default. That protects the router and the home (local) network from unauthorized access from the external network.
You can access the router's web interface from the Internet with a private and public IP address on its external (WAN) interface, which you use for your connection.
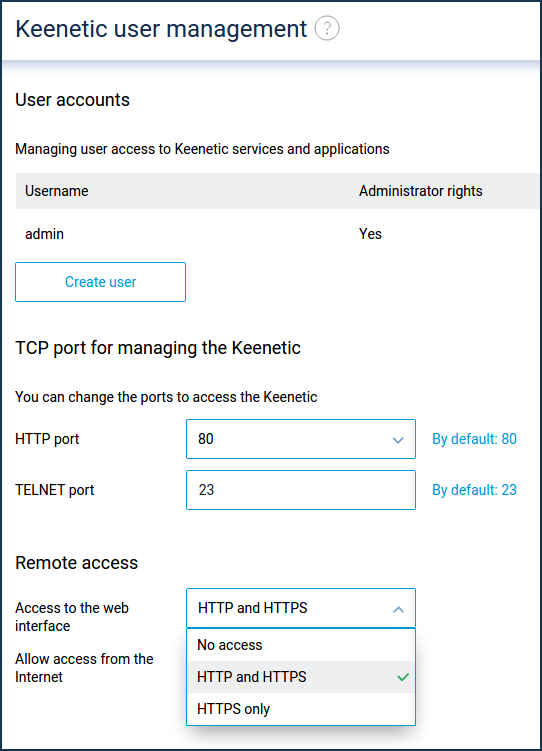
NOTE: Important! Starting with KeeneticOS 3.1, the access to router management (to its web interface) from the Internet has changed. If you didn't select 'Allow access from the Internet - via HTTP' in previous versions of KeeneticOS, you would not be able to access the web interface after updating to 3.1. The setting 'Allow access from the Internet - via HTTP' on the 'Keenetic user management' page has a priority over Firewall settings in version 3.1.
To set up remote access, you can use our domain name service KeenDNS. It will provide you with a permanent Internet address for your Keenetic device. You will be able to connect to the built-in applications of the router and open services of the home network from the Internet using your permanent domain name, such as myrouter01.keenetic.pro. Unlike other similar services, KeenDNS is entirely free and can work directly and via the cloud. In this case, remote access to the interface and built-in applications will be available even if there is no public IP address (for example, when connecting via a 3G/4G modem).
NOTE: Important! The digital certificate and the HTTPS private key are stored directly on the end device (the router). When accessing through a cloud server via the HTTPS protocol, a secure tunnel is built to the router, ensuring the safety and confidentiality of the data transmitted over the Internet. The session is established using end-to-end encryption. It means that KeenDNS cloud servers, which provide transport level of data transmission, do not have access to the information transferred between the router and the browser via HTTPS. With cloud access via HTTP, a secure channel is set between the router and the KeenDNS server using a digital KeenDNS certificate, guaranteeing data safety and protection against interception.
So, enable the KeenDNS service, create a name for the router and register it.
After registering a KeenDNS domain name, you can access the router web interface from the Internet. Launch your web browser and enter the KeenDNS name in the address bar. For example:
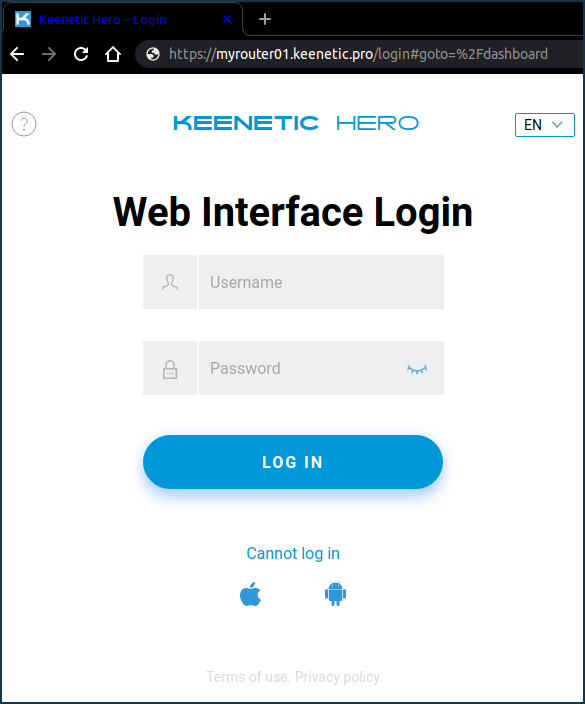
Or from a mobile device:
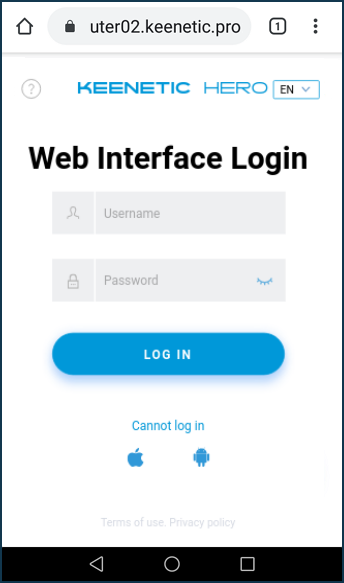
Thus, a user will be able to access the Keenetic management remotely.
You can also use one of the dynamic DNS services. But this option is applicable only if you have a public IP address on the router's external (WAN) interface. You can find more information in the article Dynamic DNS client.
NOTE: Important! Only the web interface of the Keenetic can be accessed via KeenDNS in cloud mode. You can't access the router's command-line interface (CLI) using the TELNET/SSH protocol. In the direct access mode, you can use any protocol that is not limited by your ISP to access your home network remotely.
TIP: Tip: Here is an example of a connection to the web interface that uses a standard (pre-configured) port 80.
If necessary, you can change the standard web interface management port number to another (81, 280, 591, 777, 5080, 8080, 8090, and 65080). You can do this on the 'Keenetic user management' page in the 'TCP port for managing the Keenetic' section. Now add a colon and the new port number to the router address in your web browser. For example: myrouter01.keenetic.pro:5080.
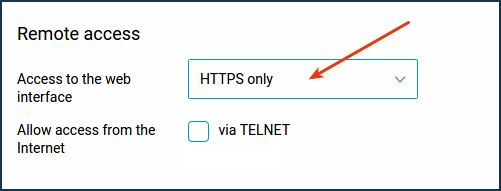
Starting with KeeneticOS 3.1, you can select 'HTTPS only' in remote access settings (on the 'Keenetic user management' page), which improves the security of access to the router's web interface.