Keenetic routers allow organizing the segmentation of home network space into isolated zones. In essence, the primary 'Home' and 'Guest,' and optional, for example, 'Smart home' and 'Children's room,' and in the office, it can be 'Accounting' and 'Administration.'
Dividing a network into isolated zones (segments) allows us to increase network security and optimize its performance. Devices in additional segments have access only to the Internet and, if necessary, to each other within a segment. Even if they are taken over by intruders or bots, all other segments will remain unavailable to them. For example, if friends come to your child, and he gives them a password to the Wi-Fi network, they will not be able to access the parents' computers, a smart home system, or video monitoring. The same applies to possible viruses and threats from guest devices. To improve performance, you can allocate some devices to a separate segment and limit their maximum speed so that they don't interfere with other devices on the network.
Using segments, you can create an additional local network. A segment is a logical interface that can include one or more available physical interfaces. Within a single segment, all interfaces are combined into a network bridge. In the segment settings, you can specify a personal name and wireless network settings, schedule, limit the speed of access to the Internet or completely prohibit it, select wired ports, configure VLAN, network addressing, DHCP server.
Let's take the example of creating an additional segment of a home network. Suppose you need to create a segment that includes a new Wi-Fi network named HOME-WIFI and ports 2, 3 of the built-in switch. The new subnet should have its DHCP server and address different from the main Home network (in our example, 192.168.2.x subnet).
On the Home network page, click on '+' to add a segment and then configure the new segment (select network ports and specify other required settings).
For example:
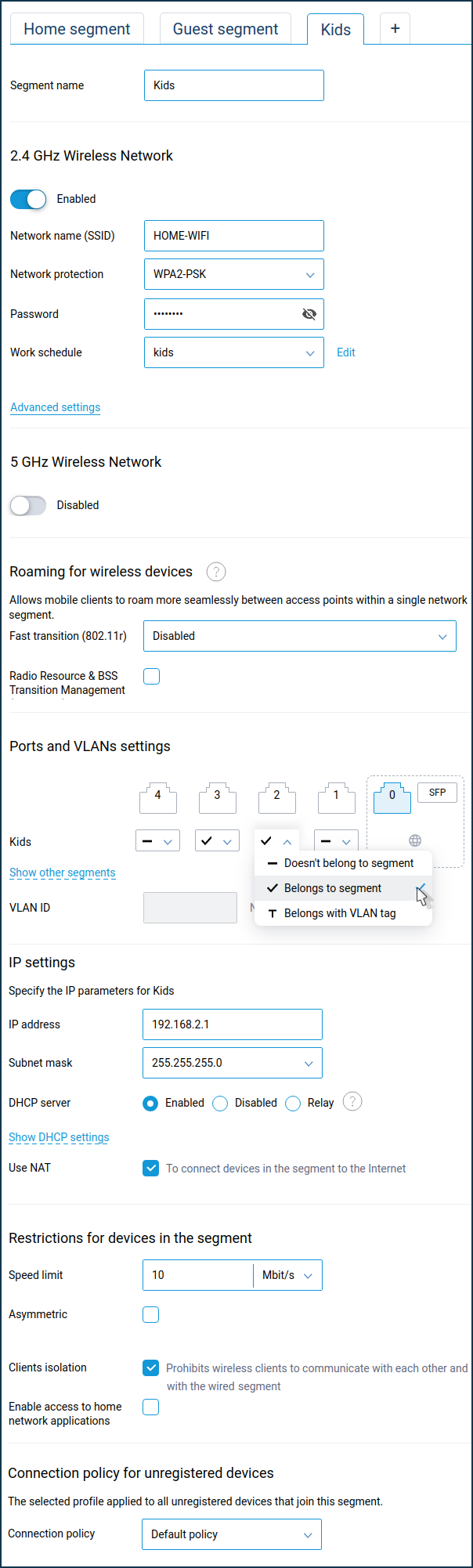
NOTE: Important! By default, access between the main home network and an additional segment is not allowed.
Important! There is a limit to the number of additional segments with Wi-Fi access points that can be created. Up to 4 access points per band can be created on the router. On a dual-band router, a maximum of 8 access points can be created - 4 in the 2.4 GHz band and 4 in the 5 GHz band. If you use the joint capability of both radio interfaces in each segment, a maximum of 4 segments can be created. When creating additional segments without Wi-Fi access points, there are no restrictions.
TIP: Note: How to allow access between segments.
There are two ways to do this:
1. Recommended method. By using firewall rules.
For the home network interface, you need to create a permissive rule by specifying the additional segment's subnet as the destination address (in our example, 192.168.2.0 with a mask of 255.255.255.0) and the protocol IP.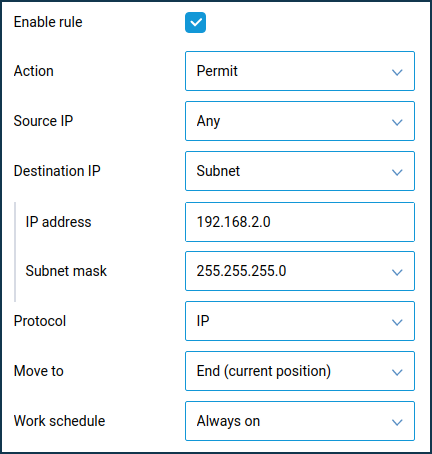
In this case, you will be able to access additional segment devices (192.168.2.x) from your home network.
If access is required from an additional segment to the home network, a similar rule should be created for the additional segment, only with the reverse destination IP address 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 for the IP protocol.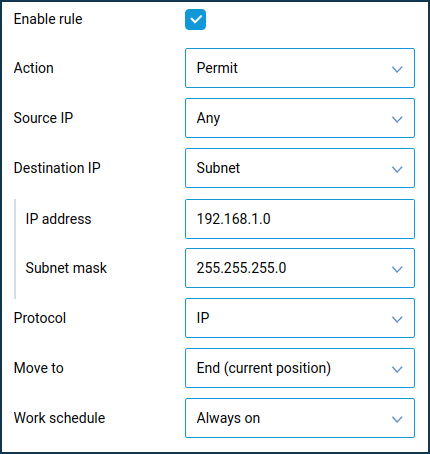
2. In Keenetic command-line interface (CLI) you can execute the commands:
no isolate-private
system configuration save
Important! Use this method with caution, as it may not be safe. Executing these commands will allow the exchange of traffic between all of the local (private) interfaces. In this case, access between the main home network and additional segments, including the guest network, will be opened.