On the 'Telephone line settings' page, specify the connection settings provided by your IP telephony service provider.
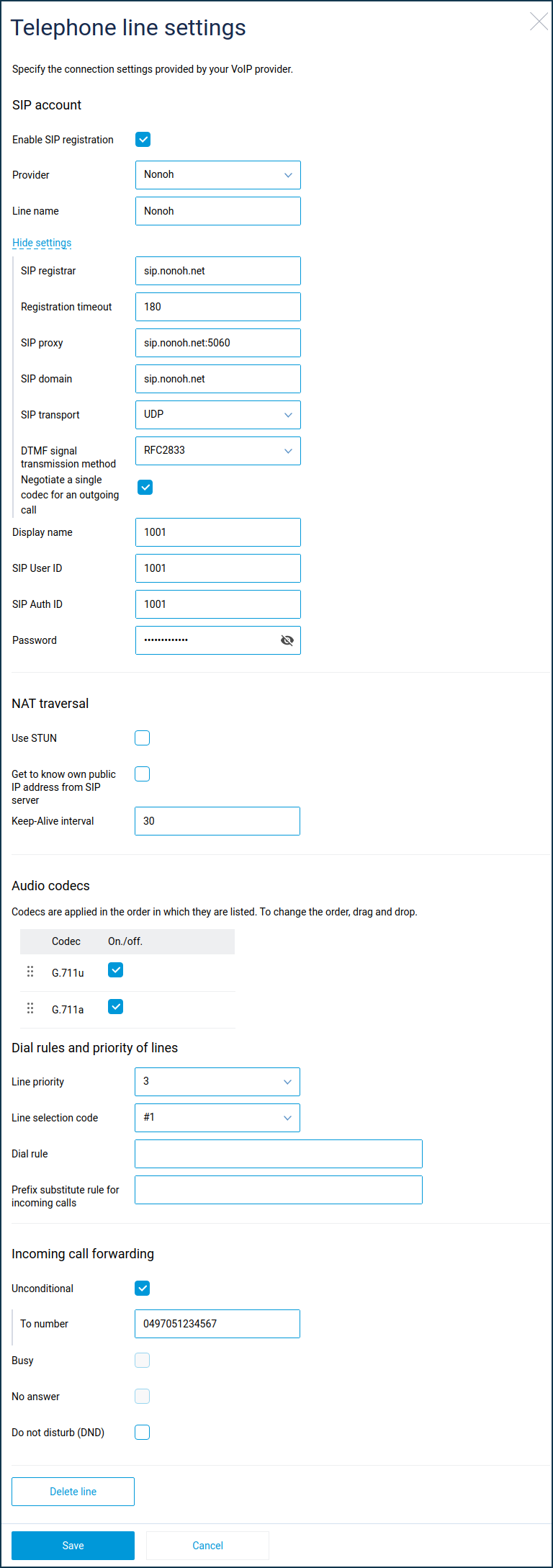
SIP account section
Enable SIP registration — SIP registration must be enabled to connect to most IP telephony operators. Disable SIP registration if you want to configure the line to connect to an operator without registration, with authentication by IP address. In addition, disabling registration allows you to set up direct calls between two Keenetic devices without using an IP telephony provider (hereinafter p2p calls).
Provider — select an IP telephony operator from the list to automatically configure a line to connect to that provider. If your ISP is not on the list, select 'Other' and configure the phone line manually. You can contact Keenetic technical support to add a provider to the list.
Line name — the name of the line can be anything. It appears in the system call log and message log entries created for incoming and outgoing external calls.
By default, some of the settings configured automatically when an operator is selected are hidden. Click 'Show settings' if you wish to configure them manually.
SIP registrar — IP address or domain name of the SIP registration server. If the server uses a non-standard port (other than 5060), specify it to the right, separated by a colon. When SIP registration is disabled, this field is not displayed.
Registration timeout — the period of validity of SIP registration on the IP telephony operator's server, after the expiry of which the registration should be resumed. The server can change this parameter during the registration process. Registration is required in order to receive incoming calls. When SIP registration is disabled, this field is not displayed.
SIP proxy — the proxy server of the IP telephony operator through which SIP signalling messages must be routed. If the server uses a non-standard port (other than 5060), specify it to the right with a colon. For p2p calls, you need to specify the IP address and port of the other Keenetic device here.
SIP domain—is the name of the SIP domain where the user is registered (right side of the SIP URI after the '@' symbol). When configuring p2p calls, the same domain (any domain) must be configured on both Keenetic devices.
SIP transport — the transport protocol (onwards: transport) used to transmit SIP signalling messages. Select the transport protocol that your IP telephony operator supports:
- UDP/UDP6 — the most commonly used transport. Supported by most SIP IP telephony servers and subscriber devices;
- TCP/TCP6 — guarantees delivery of messages, including long messages, which cannot be carried by UDP transport;
- TLS/TLS6 — enables the secure exchange of SIP signalling messages with the operator's server. It helps prevent the theft of credentials and other important information transmitted in SIP signalling messages.
UDP, TCP and TLS transports use the IPv4 network layer protocol for data transfer. When using IPv4 to communicate with an IP telephony operator's server, you should select these transports.
UDP6, TCP6 and TLS6 are UDP, TCP, and TLS transports that use the IPv6 network layer protocol for data transfer. You should select these specific transports to communicate with an IP telephony operator's server using IPv6.
Note: When communication with an IP telephony operator's server is only possible over one specific version of the IP protocol (either 4 or 6), the system automatically uses that version regardless of the selected transport. In other words, if communication is only possible over IPv4, the UDP transport will use IPv4 even if the line setting specifies UDP6.
SIP security mode — this setting is only available when the TLS transport protocol is selected. Select the security type when using TLS:
- SIP-TLS — the SIP URI scheme is used. This only uses the TLS transport to send SIP signalling between your Keenetic device and your IP telephony provider's proxy server;
- SIPS — the SIPS URI scheme is used. It is designed to ensure that secure transport protocols are used to send SIP signalling all the way between you and the remote subscriber you are talking to.
Voice transmission protocol:
- RTP — to transmit voice data using the RTP protocol only;
- RTP or SRTP — on outgoing calls, offer to use the SRTP protocol to secure voice data exchange. For incoming calls, use the protocol (RTP or SRTP) offered by the calling party;
- SRTP — use only the secured SRTP protocol. Reject incoming calls if the calling party offers to use unsecured RTP.
DTMF signal transmission method — during an established telephone connection, it is sometimes necessary to additionally dial the caller's extension number, voicemail control codes, etc. When the keypad buttons are pressed, the corresponding DTMF signals (0, 1...9, # and *) are transmitted to the remote party over the VoIP connection using one of three methods:
- RFC2833 — transmission by RTP protocol messages;
- SIP Info — SIP INFO request transmission;
- Inband — transmission in the media stream together with voice.
Select the DTMF transmission method that your IP telephony operator supports.
Display name — the name that is displayed on the called party's phone when an outgoing call is made.
SIP User ID — the SIP User ID (the left side of the SIP URI before the '@' symbol).
SIP Auth ID — the name used when authenticating to the IP telephony operator's servers. This field is not displayed when SIP registration is disabled.
Password — the password used when authenticating to the IP telephony operator's servers. This field is not displayed when SIP registration is disabled.
NAT traversal section
Use STUN — this option should be used when the Keenetic device is connected to the IP telephony operator's public SIP server via a NAT router and has a local IP address on the WAN interface. It allows you to receive the external IP address and NAT UDP ports associated with the local SIP and RTP ports of Keenetic Phone Station from the STUN server. The received data is placed in the Via, Contact, Connection Address and Media Port headers of SIP signalling messages. It should be noted that STUN technology does not work with symmetric type NAT.
Get to know own public IP address from SIP server — with this option, Keenetic Phone Station receives the IP address (or NAT IP address) from the SIP registration server and overwrites the relevant fields in the Via, Contact and SIP/SDP headers with it. This ensures two-way audibility and successful exchange of SIP signalling messages. Activate this option when a secondary channel such as a VPN tunnel is used to communicate with the server or when there is a symmetrical NAT between the Keenetic router and the public IP telephony server with which STUN technology does not work.
Keep-Alive interval — Keenetic periodically sends Keep-Alive messages to the SIP proxy signal port at a set interval to keep an open connection to the server via NAT.
This is necessary to ensure that incoming calls are received from the server.
Audio codecs section
When used with the Keenetic Linear adapter, Keenetic Phone Station supports the following codecs:
- G.711u
- G.711a
Codec priority corresponds to its position in the list, i.e. the codec in the top position has the highest priority. Codec priorities are taken into account for outgoing calls. The called party selects the codec with the highest priority that it supports. You can change the codec priority by dragging the line to the desired position. To drag and drop, use the special marker located at the beginning of each line.
The codecs can be turned on and off. The switched off codecs are not used for voice communication.
Dial rules and priority of lines section
Line priority — the telephone line priority number. The higher the number, the higher the priority. Priorities are taken into account when selecting a line for an outgoing call. The telephone exchange selects the line with the highest priority among those that are allowed for this telephone and have appropriate dialling rules.
Line selection code — line selection code #0...#9 allows you to select the desired line for an outgoing call. To select a line, you need to dial its code, then the subscriber's number. When you select a line with the code, the dial rules are ignored, and you can call a number that does not comply with the dial rules of that line. Only lines that are allowed for the phone can be dialled with the code. To prohibit line selection using a code, select 'no' from the drop-down list of codes.
Dial rule — the dial rule describes the numbers for which outgoing calls are allowed through this line. In the absence of a dial rule, any numbers are allowed to be called.
When an outgoing call comes in, the Phone Station selects the line with the highest priority among those that have dial rules to which the dialled number corresponds. If the number does not match the dial rules, the line without dial rules with the highest priority is selected. A line without dial rules always has a lower priority than any line with dial rules. Only a line in which outgoing calls are allowed through this port can be selected for a call.
Dial rule syntax:
- 01234567890*#+ABCD — characters allowed by dialling rules;
- T — waiting for the next digit of the number;
- x — any digit from 0 to 9;
- [146] — any of the digits in square brackets (1, 4 or 6);
- [1-6] — any one of the digits in range, specified in square brackets (1,2,3,4,5 or 6);
- (8>+7) — replacement/substitution/deletion. To the left of the '>' character is a sequence of digits to be replaced by the sequence to the right of the '>'. If only the sequence on the left is specified, it will be deleted from the dialled number. If only the sequence to the right is specified, it will be added. The expression must be enclosed in parentheses.
- 2. — the digit to the left of the dot is repeated any number of times.
The '|' character separates two or more rules in a string.
Examples of dial rules:
- +749[589]xxxxxxxx — any number of seven digits prefixed with '+7495', '+7498' or '+7499'.
- 8[49]xxxxxxxxxx — any number with 11 digits, the first digit of which is '8' and the second one is "4" or "9.
- 10xx — any four-digit number, the first digit of which is '10'.
- *xx# — a four-digit sequence, in which the first character is '*', followed by any two digits and the character '#'.
- [1-79]xxxxxx — any number with seven digits, where the first digit is any digit, except 8;
- x. - any number consisting of digits from 0 to 9.
- 0T|00T|000 — the numbers 0, 00 or 000. The symbol 'T' is used to wait for dialling to continue after dialling 0 and 00. It should be used when you want to dial numbers in conversational mode (press the call button, then dial the number).
- (8>+7)x.—in any number, the first digit of 8 will be replaced by +7.
- (*2>84951234567) — dialling *2 will send a call to 84951234567. This is how you can set up speed dial.
- 8[49]xxxxxxxxxx||10xx|*xx# — the three rules discussed above are written in one line separated by '|'. The Phone Station checks these rules one by one, from left to right.
Prefix substitute rule for incoming calls — allows you to replace or delete individual digits or groups of digits in a caller number that appears on the telephone display when a call comes in. The symbol '>' is used for replacement. To the left of the '>' must be a sequence of digits to be replaced by the sequence to the right of this symbol. The replacement expression must be enclosed in parentheses. There can be more than one replacement expression in a prefix replacement rule. Otherwise, the prefix substitution rule has the same syntax as the corresponding set rule discussed above.
An example of a prefix substitution rule:
- (8>)49(5>9)x. — In the numbers, which begin with the digits 8495, the digit 8 is deleted, the digit 5 is changed to 9, and the rest of the number is left unchanged. The resulting number is shown on the telephone display.
Note: What is the prefix substitution rule used for? In some cases, for incoming calls, the calling numbers are in a format that is not compatible with the dialling rules of the IP telephony operator. This makes it impossible to call the caller back to the number that was shown on display. For example: during an incoming call, +491761234567 is displayed on the phone display but to call back the given subscriber, you need to dial 01761234567.
In this case, the prefix replacement rule (+49>0)x. can replace +49 in the caller's number with 0. With this rule, the number 01761234567 appears on the phone display when there is an incoming call and is compatible with the operator's dial rules.
Incoming call forwarding — this function allows you to forward incoming calls to certain numbers under certain conditions.
Activate the option corresponding to the required forwarding condition; on the right, indicate the telephone number to which you want to forward incoming calls.
Call forwarding conditions:
- Unconditional — the call forwarding is always performed. When unconditional forwarding is selected, other types of forwarding do not work. When a call is forwarded unconditionally, you do not receive a call on the phones. Information about forwarded calls is recorded in the call history and the system log;
- Busy — calls are forwarded when the handsets for which you have allowed incoming calls from this line are busy in a call;
- No answer — the call forwarding is performed if an incoming call is not answered within the time interval. This interval (in seconds) must be specified in the appropriate field to the right of the call forwarding number.
Note: Keenetic Phone Station allows you to receive a second call during a call. This means that the busy condition is met when each of the handsets allowed to receive an incoming call is already involved in two calls. This is possible when one of the calls is put on hold.
When a call is forwarded, Keenetic Phone Station sends a special SIP message to the calling party with the SIP URI and the forwarding number. All further actions on subscriber connection to this number are performed by the subscriber's equipment and/or IP telephony operator's server.
Do not disturb (DND) — enable this option if you do not want to be disturbed by incoming calls. When DND is activated, calls are not received on the phones, callers are notified that you are busy, and information about missed calls is recorded in the call history and system log.
Delete line — press this button if you wish to delete the line. Once you have confirmed, the line will be permanently deleted, and you will no longer be able to use the IP telephony service of this operator.