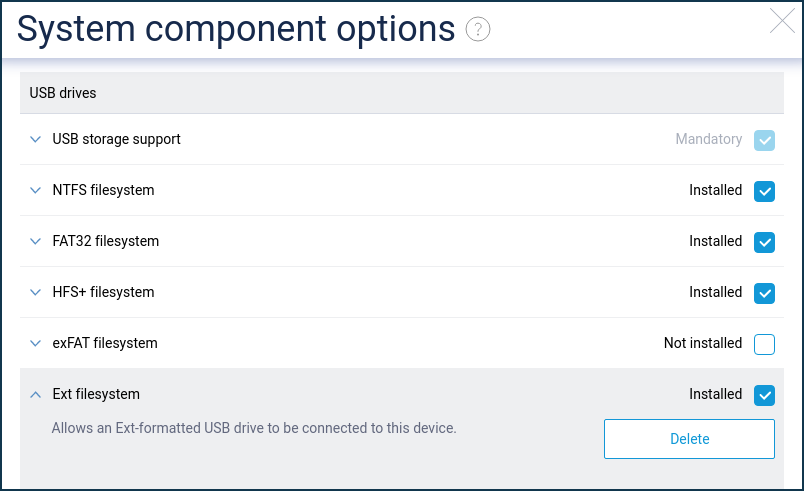
You can use the ext4 file system on USB drives connected to your Keenetic router.
You must first install the' Ext filesystem' component for your Keenetic router to work with the ext4 file system. You can do this from the 'General system settings' page under 'Component options' by clicking on 'Component options'.
Ext4 is one of the major file systems, used primarily in operating systems with a Linux kernel. More information can be found on the Internet: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ext4.
Compared to ext3, ext4 supports larger file sizes and is a faster, more efficient and more stable file system.
NOTE: Important! The 32-bit systems used in all Keenetic models (except the Peak KN-2710, which uses ARM64) have kernel-level restrictions on mounting and handling multi-terabyte data arrays. In the EXT4 file system, drives up to 16 TB can be connected. If you mount a drive larger than 16TB, you can divide it into 2 partitions (the partition must be no larger than 16TB) and then these partitions will mount successfully in the system.
We recommend formatting a drive in the ext4 file system from a GNU/Linux distribution by the operating system or using special programs and utilities for disk management.
NOTE: Important! Formatting the drive will erase all data on the selected storage volume. Be sure to copy the data from the drive before formatting.
Formatting in Linux
Usually, a GNU/Linux OS distribution has a graphical utility for formatting USB drives and hard drives (e.g. in Linux Mint — USB Stick Formatter utility, in Ubuntu — Gnome Disk Utility, etc.) as well as the GParted drive management utility. You can use these tools to format a drive or format it from the command line.
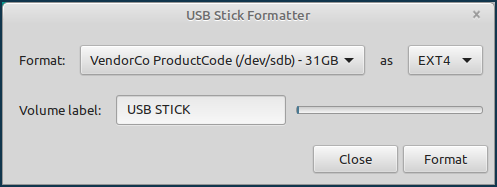
Here is an example of formatting a USB flash drive using the USB Stick Formatter utility.
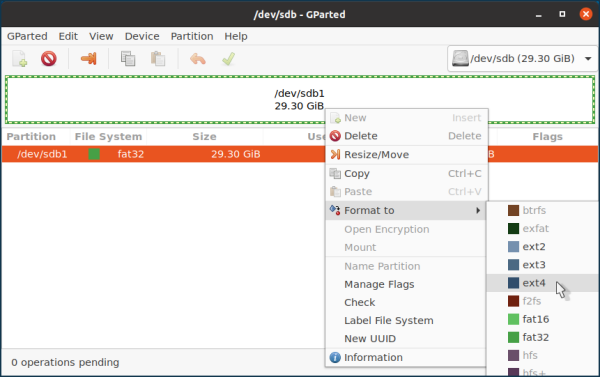
A universal way to format a USB drive is to use the GParted drive management utility. Usually, it is already installed in an OS, but if necessary, it can be installed from the official repositories (run sudo apt install gparted or sudo yum install gparted depending on the distribution).
Launch GParted. Select the required device in the upper right corner (you can identify your drive by label, size or file system). Unmount the drive so that you can format it.
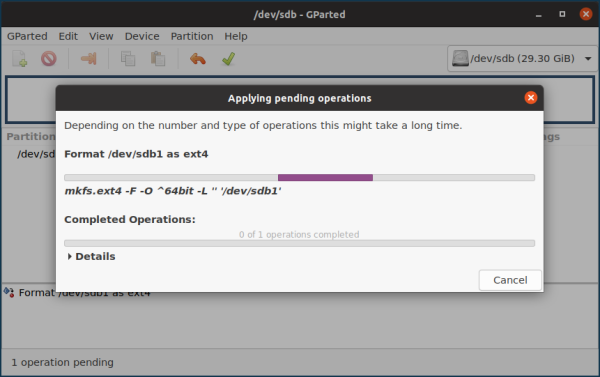
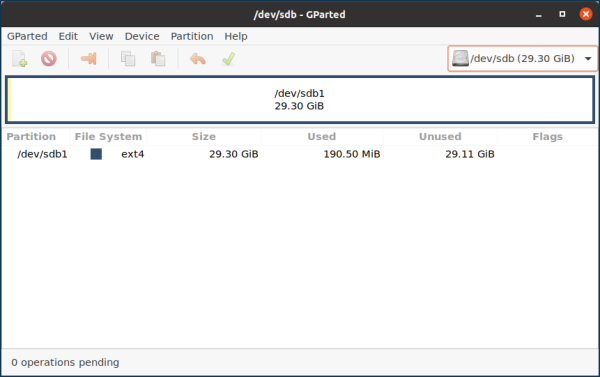
You can also format with special commands via Terminal.
One of the ways is as follows:
Execute the df command and define the location of the connected drive (/dev/sdb, /dev/sdc, ...). In our example, let's suppose that the flash drive is in /dev/sdc1.
Then it should be unmounted. You can do it using a command
sudo umount /dev/sdc1
Now, to format it into an ext4 file system labelled 'USB', execute the command
sudo mkfs.ext4 -n 'USB' -I /dev/sdc1
NOTE: Important! 1. The ext4 file system drive cannot be used in Windows. If you need to mount an ext4 drive in Windows, you can use the special ext2fsd driver developed by the community of open-source software for ext file systems.
2. By default, 5% of the partition or drive is reserved for the EXT4 file system. For example for the root partition. On Linux you can disable partition reservations with the tune2fs utility: sudo tune2fs -m 0 /dev/<xxx></code>, where 0 disables block reservations, and 5 sets the reservation to 5%. See the link for details.
Formatting in Windows
As described above, formatting the drive in the ext4 file system is recommended from the GNU/Linux distribution. However, you can format from Windows if needed. For example, you can use MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition or Paragon Partition Manager Free.
Formatting in MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition:
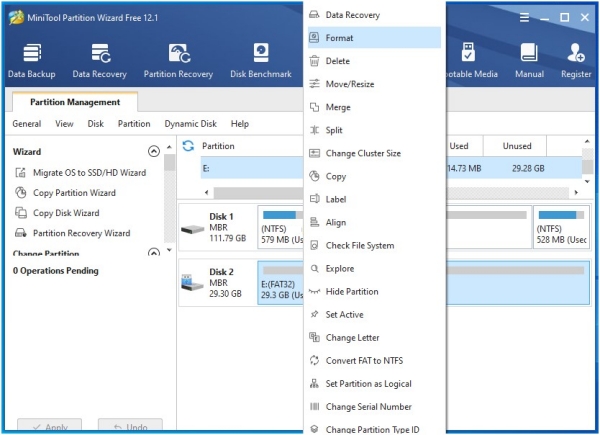
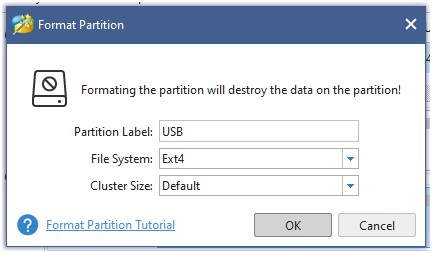
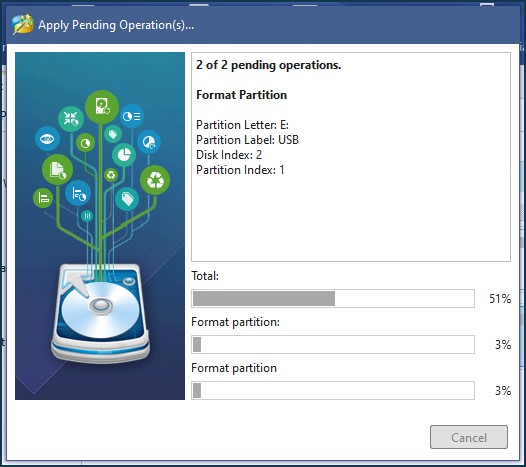
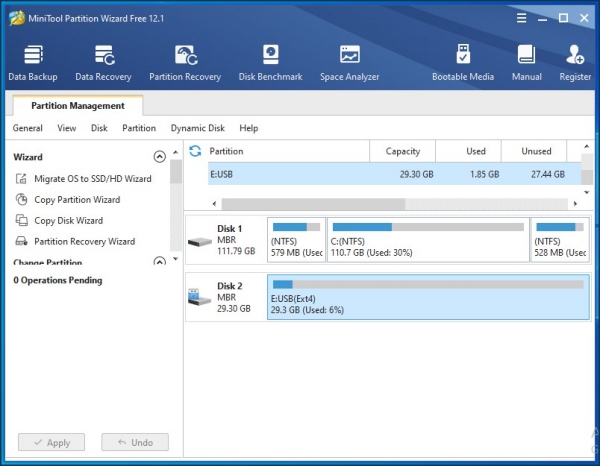
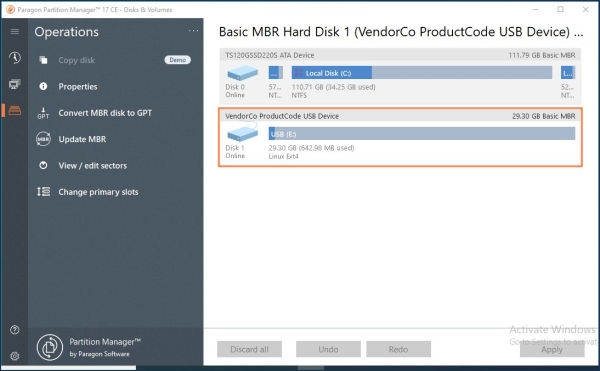
Formatting in Paragon Partition Manager Free:
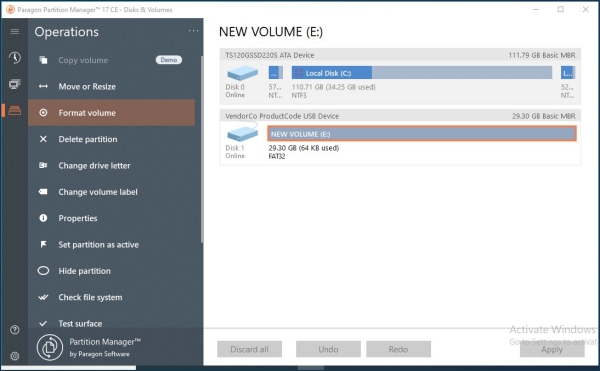
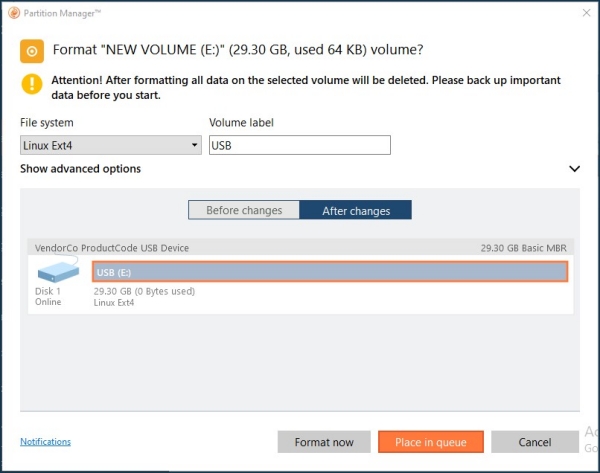
Connect the prepared drive with the EXT4 file system to the router's USB port. The drive should appear in the 'Applications' page under 'USB Devices'.
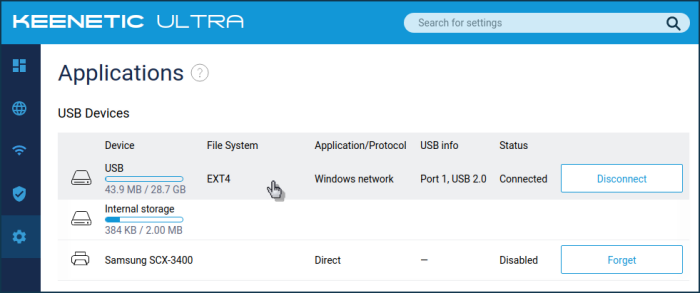
If the router does not detect the USB drive, check if the 'Ext filesystem' operating system component is installed.