NOTE: Important! If you want to configure a Keenetic router as a VPN server, make sure that it has a public IP address, and when using the KeenDNS service, that it works in the 'Direct access' mode. If any of these conditions are not met, connecting to such a server from the Internet will be impossible.
The L2TP/IPSec VPN server on Keenetic routers can be configured by following the L2TP/IPSec VPN server instruction.
To connect to the server, create an L2TP/IPSec VPN connection on your iPhone/iPad.
Go to 'Settings' in the 'General' section. Click on 'VPN'.
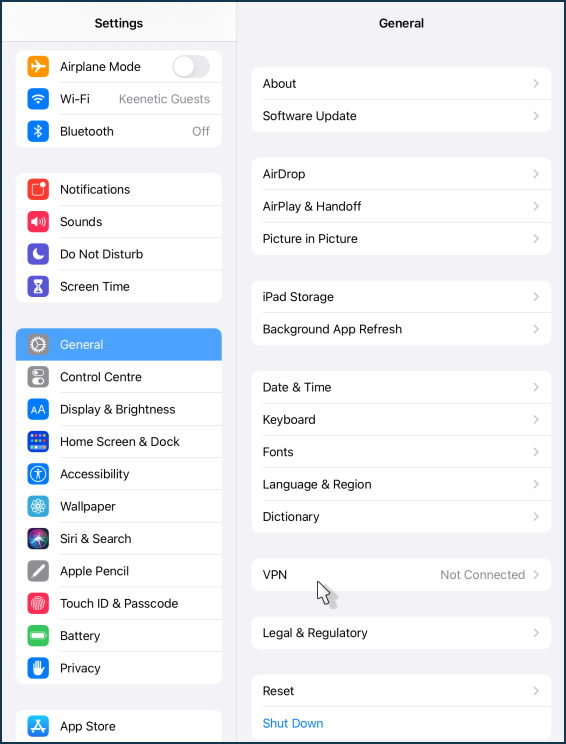
Click on ' Add VPN Configuration...'.
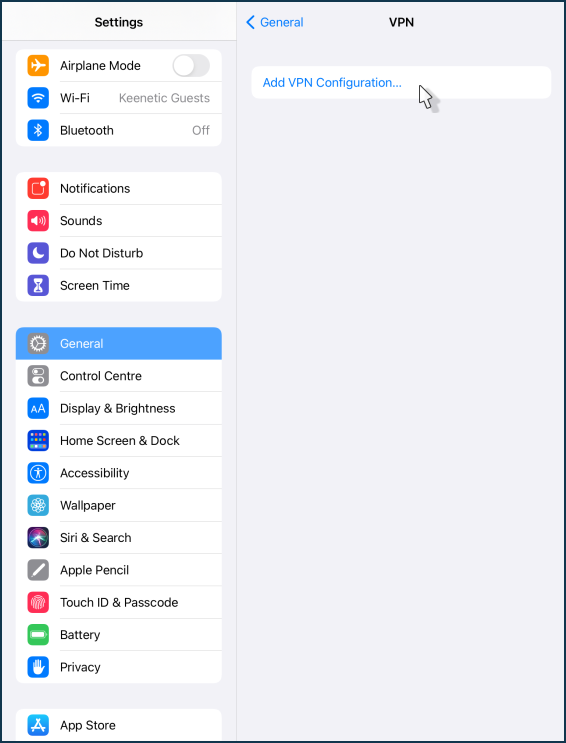
Click on the 'Type' field.
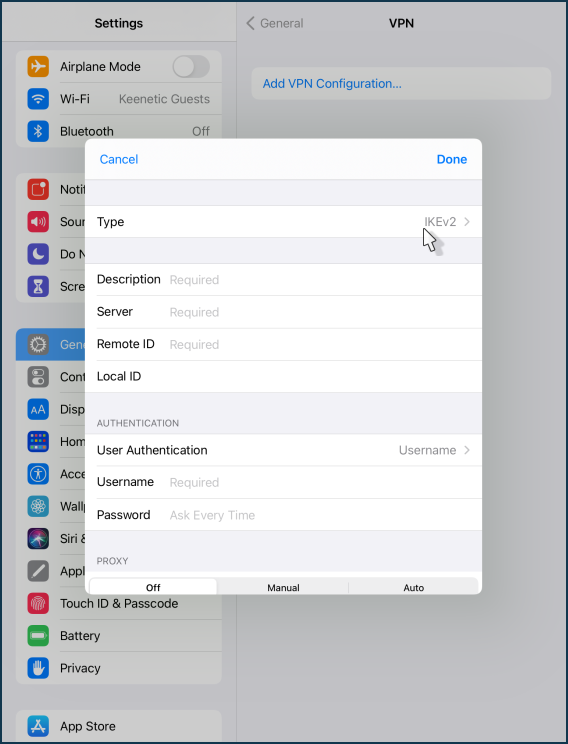
Select 'L2TP' connection type.
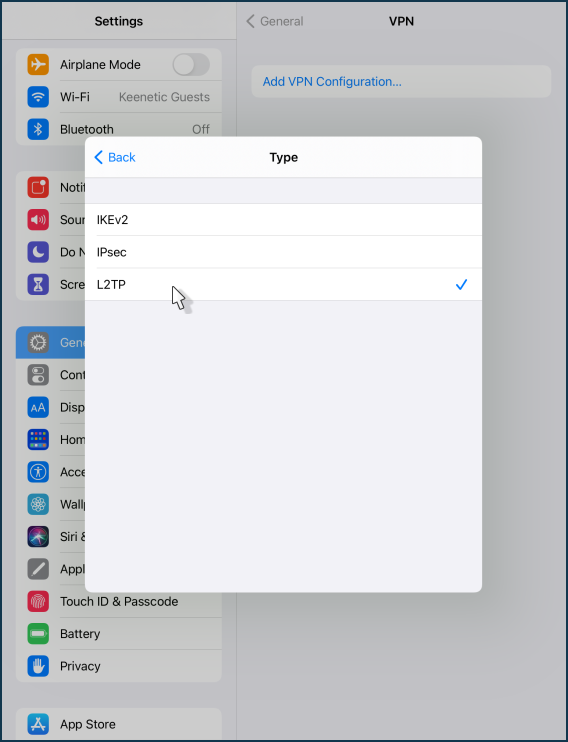
Then set up the VPN connection. Specify the 'Description', enter the domain name or public IP address of the Keenetic router. Specify the account that is authorized to access the VPN in the Keenetic settings and its password. Enter the 'Secret' that was set when the connection was created on the Keenetic VPN server. To save the settings, click 'Done' in the upper right corner of the screen.
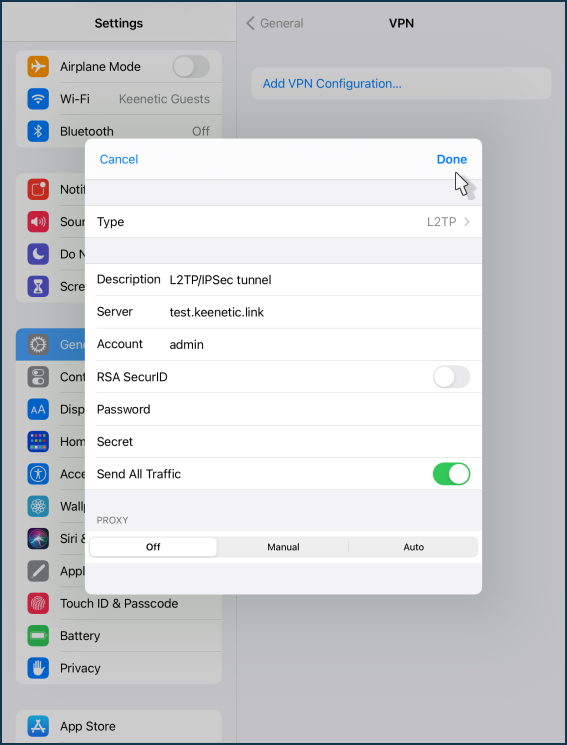
These settings are enough to access the Keenetic home network.
NOTE: Important! By default, the 'Send All Traffic' option is enabled in the VPN settings. In this case, the iPhone/iPad will send all traffic to the VPN tunnel, including for Internet access via Keenetic router.
The configuration of the L2TP/IPsec VPN connection is complete.
All that remains is to move the switch to the 'Connected' state.
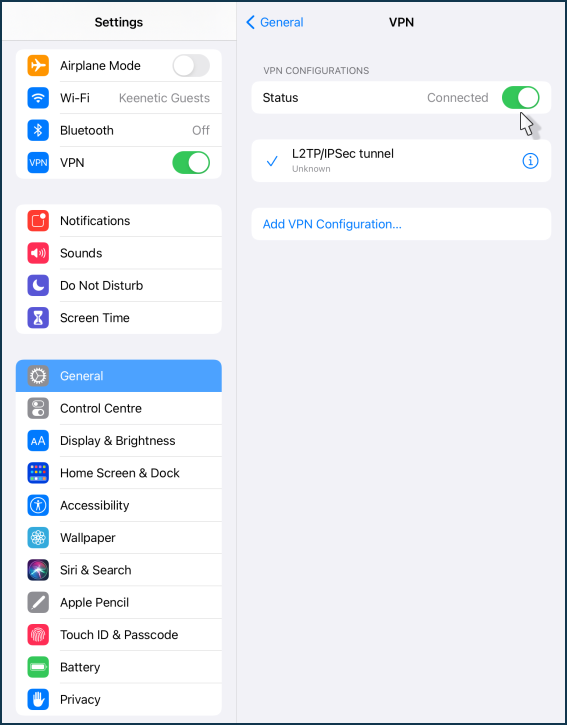
Once connected, click on the '(i)' icon to verify that the connection to the server has been established.
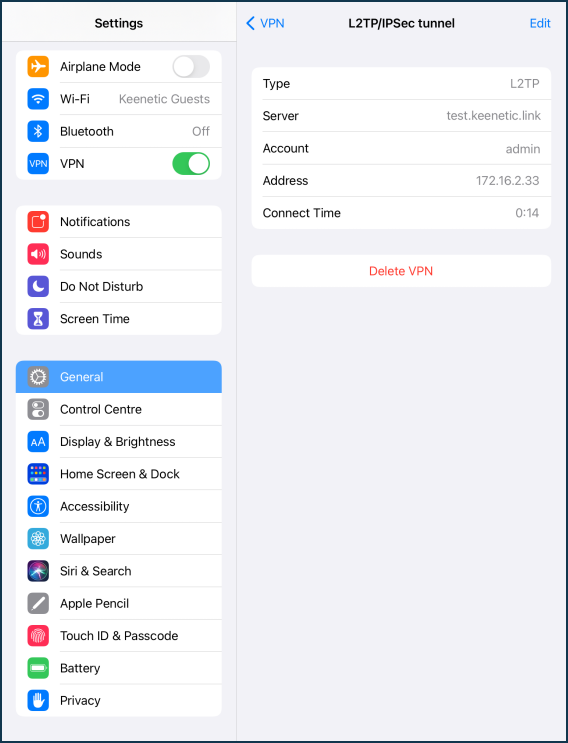
Note
If you have your Keenetic connected via another router with a public IP address, you have to configure port forwarding on that router to be able to connect from the Internet to a VPN server on your Keenetic. L2TP/IPSec requires UDP 500 and UDP 4500 forwarding. Another option is to forward all ports and protocols, which is called DMZ on some routers.
A typical example of such a router is a CDC Ethernet modem. It can get a public address from the ISP and give a private address to your Keenetic. Port forwarding setup depends on the modem. There are some that forward all ports without any extra setup. Others have this setting in their own web interface. And there are some where it is not available at all.
Another example of such a router is an optical GPON terminal installed at the flat. In such devices, the forwarding is configured in their web interface.
If the forwarding is set up correctly, you can try to establish a VPN connection with the external public IP address of such a router. It will forward it to the Keenetic's private address.